What is an Add-In?
A spreadsheet add-in is something added to a spreadsheet application to give it additional functionality. Excel ships with several add-ins. Examples include the Analysis ToolPak (which adds statistical and analysis capabilities) and Solver (which performs advanced optimization calculations).
Excel Add-in include Standard add-ins, COM add-ins and Office add-ins. Be aware that COM add-ins and Office add-ins can not be created with VBA. You need either Visual Basic.NET or Visual C++ to create COM add-ins. You use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create Office add-ins.
Excel also supports Component Object Model (COM) add-ins. These files have a .dll or .exe file extension. A COM add-in can be written so that it works with all Office applications that support add-ins. An additional advantage is that the code is compiled, so the original source isn't viewable. Unlike XLAM add-ins, a COM add-in can't contain Excel sheets or charts. COM add-ins are developed in Visual Basic .NET. Discussion of creating COM add-in procedures is well beyond the scope of this book.
Office add-ins are applications that provide expanded functionality to a sheet. Like Excel add-ins, once Office add-ins are installed, they're always available. But unlike Excel add-ins, the Office add-ins have limited interaction with sheets and do not use VBA.
An Office add-in consists of a web app and a manifest file. The web app can simply be an HTML file that provides the user interface on a task or content pane accompanied by a CSS file to provide styles for the HTML file. Or you can include interactivity by adding a JavaScript file. The manifest is an XML file and is used to register the Office add-in with Excel.
Add-in vs. standard workbook
You can create add-ins from Excel workbook files without additional software or programming tools. An Excel add-in is basically a normal XLSM workbook with the following differences:
- The IsAddin property of the ThisWorkbook object is
True. By default, this property isFalse. - The workbook window is hidden in such a way that it can't be unhidden by choosing the View > Window > Unhide command. This means you can't display worksheets or chart sheets contained in an add-in unless you write code to copy the sheet to a standard workbook.
- You install and uninstall add-ins by using the Add-ins dialog box. When an add-in is installed, it remains installed across Excel sessions.
- The Macro dialog box (invoked by choosing Developer > Code > Macros or View > Macros > Macros) doesn't display the names of the macros contained in an add-in.
- Generally, custom functions work only in the workbook in which they are defined. A custom function added to an add-in is available to all open workbooks.
- Usually, You can bypass your
Workbook_Opencode by holding down the Shift key while opening the workbook. With an add-in, they cannot bypass theWorkbook_Opencode in this manner. - After you use the Add-ins dialog box to install an add-in (by selecting File, Options, Add-Ins, Manage Excel Add-Ins, Go), the add-in will always be loaded and available.
- Programs in an installed add-in can still run even if the macro security level is set to disallow macros.
- An add-in isn't a member of the Workbooks collection. Rather, it's a member of the AddIns collection. However, you can access an add-in through the Workbooks collection.
About Excel Add-ins Manager
You can install and uninstall add-ins by using Excel's Add-ins dialog box. Which you access by using any of the following methods:
- Launch Excel, then choose Developer > Add-ins group > Excel Add-ins to launch the "Add-ins" dialog box. If you don't find Developer tab, please read: Introduction to the Developer tab
- Choose File > Options and select the Adds-ins item in the left-hand pane, In the Manage drop-down list at the bottom of the right-hand pane, select Excel Add-ins, then click the Go button.
You can install an add-in by selecting its check box, and you can uninstall an installed add-in by removing the check mark. To add an add-in to the list, use the Browse button to locate its file.
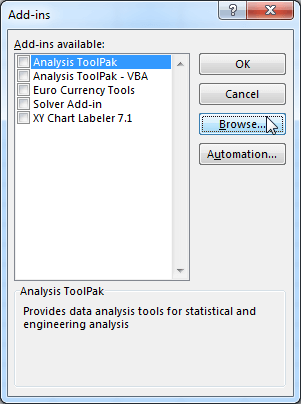
By default, the Add-ins dialog box lists files of the following types:
- XLAM: An Excel 2007 or newer add-in created from an XLSM file
- XLA: A pre–Excel 2007 add-in created from an XLS file
- XLL: A stand-alone compiled DLL file
If you click the Automation button, you can browse for COM add-ins. Note that the Automation Servers dialog box will probably list many files, including COM add-ins that don't work with Excel.
The Add-in Manager stores the installed status of the add-ins in the Windows Registry when you exit Excel. Therefore, all add-ins that are installed when you close Excel are automatically opened the next time you start Excel.