Sometimes you may need to go into your folder, open each workbook, edit, save it, close the workbook, and then open the next one. Opening each workbook in a folder or directory is typically a time consuming manual process. This little macro takes care of that annoyance.
Open All Workbooks in a Folder
'---------------- Modules ----------------
Sub OpenAllWorkbooks()
'Step 1:Declare your variables
Dim MyFiles As String
'Step 2: Specify a target folder/directory, you may change it.
MyFiles = Dir("D:\Temp\*.xlsx")
Do While MyFiles <> ""
'Step 3: Open Workbooks one by one
Workbooks.Open "D:\Temp\" & MyFiles
'run some code here
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=True
'Step 4: Next File in the folder/Directory
MyFiles = Dir
Loop
End SubHow This Macro Works
In this Macro, we use the Dir function to enumerate through all the .xlsx files in a given directory, capturing each file’s name. Then we open each file, run some code, and finally save and close the file.
- Step 1 declares the MyFiles string variable that will capture each file name that is in the enumeration.
- In Step 2, the macro uses the Dir function to specify the directory and file type we are looking for. Note that the code here is looking for *.xlsx. This means that only .xlsx files will be looped through. If you are looking for .xls files, you need to change that (along with the directory you need to search). This macro passes any file name it finds to the MyFiles string variable.
- Step 3 opens the file, does some stuff (this is where you would put in any macro code to perform the desired actions), and then we save and close the file. In this simple example, we are calling a message box to show each file name as it opens.
- The last step of the macro loops back to find more files. If there are no more files, the MyFiles variable will be blank. If that is the case, the loop and macro end.
How to Use This Macro
Most VBA code should be placed in Standard Modules unless specified.
If you see a comment '------------------ Modules------------------ in the code header that means put the code in a Standard Module. For more information, learn this course: Where should I put the Excel VBA code?
The following steps teach you how to put VBA code into a Standard Module:
- Activate the Visual Basic Editor by pressing ALT + F11.
- Right-click the project/workbook name in the Project Window.
- Choose Insert -> Module.
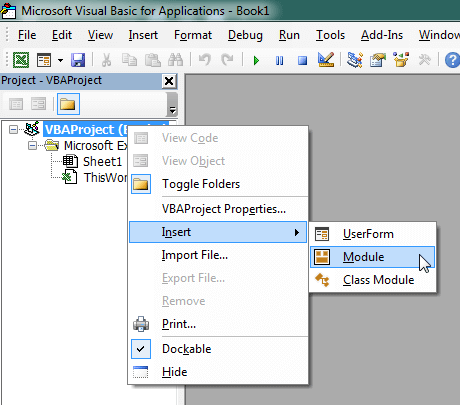
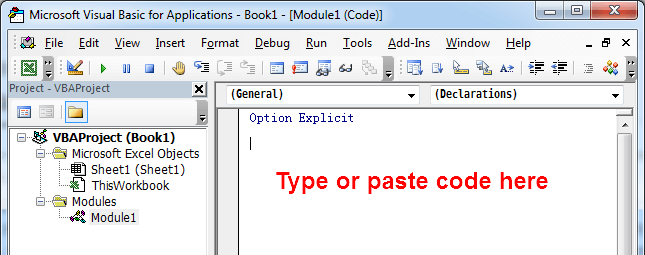
- Type or paste the code in the newly created module. You will probably need to change the sheet name, the range address, and the save location.
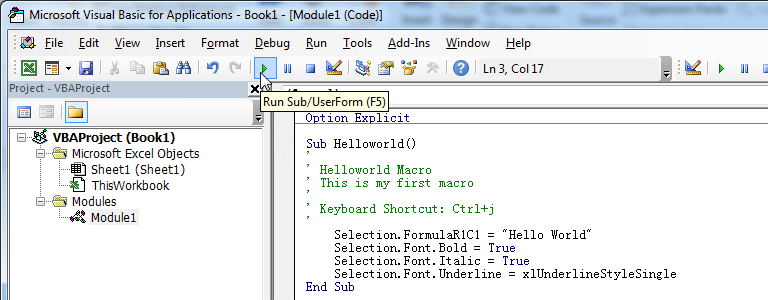
- Click Run button on the Visual Basic Editor toolbar.
- For more information, learn this course: Programming with Excel VBA