Suppose you want to send a demo file for users to check, but you don't want it to be used more than a certain number of times. There are many possible ways to do this, but here I'll show you some simple VBA statements to use, called CustomDocumentProperties.
Limit The Number Of Times Workbooks Can Be Used
This VBA code limits the workbook can be opened three times, after which the workbook is automatically deleted.
'------------------ ThisWorkbook ------------------
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Dim intOpenTimes As Integer
On Error Resume Next
With ThisWorkbook
'Add a Custom Document Property named "OpenTimes"
.CustomDocumentProperties.Add _
Name:="OpenTimes", _
LinkToContent:=False, _
Type:=msoPropertyTypeNumber, _
Value:=0
intOpenTimes = .CustomDocumentProperties("Opentimes").Value + 1
If intOpenTimes > 3 Then 'Limit 3 times
.Saved = True 'Close the "save your changes" warning
.ChangeFileAccess xlReadOnly 'Changes the access permissions
Kill .FullName 'Delete the file
.Close False 'Discards any changes
Else
.CustomDocumentProperties("Opentimes").Value = intOpenTimes
.Save 'Save this workbook
End If
End With
End Sub
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeSave(ByVal SaveAsUI As Boolean, Cancel As Boolean)
ActiveWorkbook.RemovePersonalInformation = False 'Remove Document Inspector Warning
End SubHow This Macro Works
Line 5 code: tell Excel to Resume on Error.
Line 9 code: use Add method to add a Custom Document Property named "OpenTimes".
Line 17 code: limits the workbook can be opened three times.
Line 18 code: use Saved property to close the "save your changes" warning.
Line 19 code: use ChangeFileAccess method to change the file access permissions to Read Only.
Line 20 code: use Kill statement to delete the file.
Line 21 code: use Close method to close this workbook and discards any changes.
Line 24 code: use Save method to save this workbook.
Download
Examples of CustomDocumentProperties
Update Custom Document Property
Public Sub updateCustomDocumentProperty(strPropertyName As String, _
varValue As Variant, docType As Office.MsoDocProperties)
On Error Resume Next
ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties(strPropertyName).Value = varValue
If Err.Number > 0 Then
ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties.Add _
Name:=strPropertyName, _
LinkToContent:=False, _
Type:=docType, _
Value:=varValue
End If
End Sub
Set Custom Document Properties
Sub test_setCustomProperties()
updateCustomDocumentProperty "OpenTimes", 0, msoPropertyTypeNumber
updateCustomDocumentProperty "my_API_Token", "AbCd1234", msoPropertyTypeString
updateCustomDocumentProperty "my_API_Token_Expiry", #8/31/2019#, msoPropertyTypeDate
End Sub
Get Custom Document Properties
Sub test_getCustomProperties()
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties("my_API_Token") & vbLf _
& ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties("my_API_Token_Expiry")
End Sub
List Custom Document Properties
Sub listCustomProperties()
Dim prop As DocumentProperty
For Each prop In ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties
Debug.Print prop.Name & " = " & prop.Value & " (" & Choose(prop.Type, _
"msoPropertyTypeNumber", "msoPropertyTypeBoolean", "msoPropertyTypeDate", _
"msoPropertyTypeString", "msoPropertyTypeFloat") & ")"
Next prop
End Sub
Delete Custom Document Properties
Sub deleteCustomProperties()
On Error Resume Next
ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties("OpenTimes").Delete
ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties("my_API_Token").Delete
ActiveWorkbook.CustomDocumentProperties("my_API_Token_Expiry").Delete
End Sub
How to Use This Macro
Most VBA code should be placed in Standard Modules unless specified.
If you see a comment '------------------ Modules------------------ in the code header that means put the code in a Standard Module. For more information, learn this course: Where should I put the Excel VBA code?
The following steps teach you how to put VBA code into a Standard Module:
- Activate the Visual Basic Editor by pressing ALT + F11.
- Right-click the project/workbook name in the Project Window.
- Choose Insert -> Module.
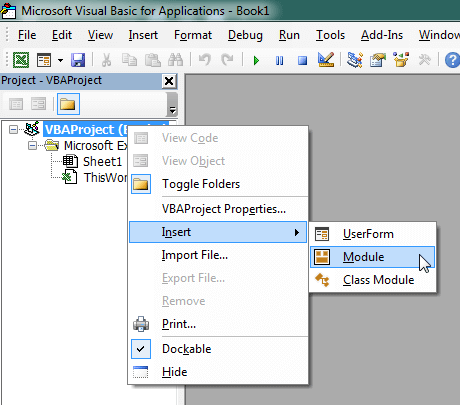
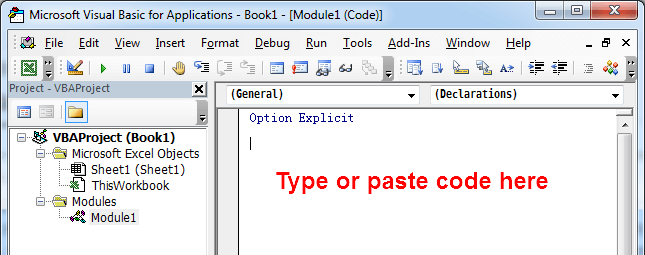
- Type or paste the code in the newly created module. You will probably need to change the sheet name, the range address, and the save location.
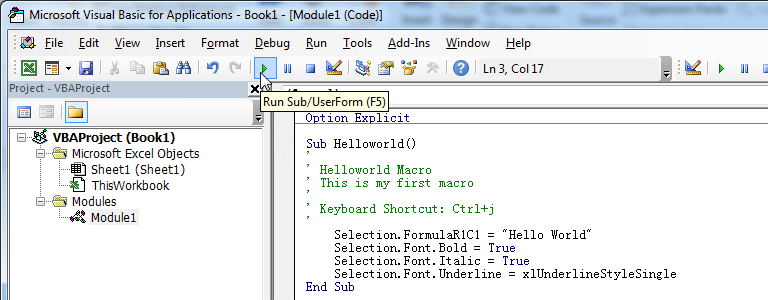
- Click Run button on the Visual Basic Editor toolbar.
- For more information, learn this course: Programming with Excel VBA