When you looking at a large worksheet with numerous data, it would be nice if Excel automatically highlighted the active cell row and column so that you can easily read the data to avoid misreading them. The following VBA code examples show ways to highlight the active cell or the rows and columns that contain the active cell.
Highlight the Active Cell
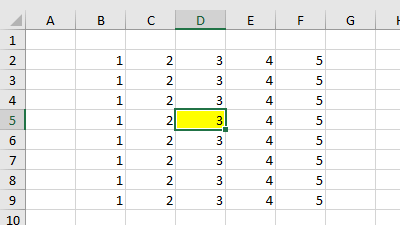
The following VBA code example clears the color in all the cells on the worksheet by setting the ColorIndex property equal to 0, and then highlights the active cell by setting the ColorIndex property equal to 6 (Yellow).
'------------------ Worksheet ------------------
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
' Clear the color of all the cells
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
' Highlight the active cell
Target.Interior.ColorIndex = 6
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubHighlight the Entire Row and Column
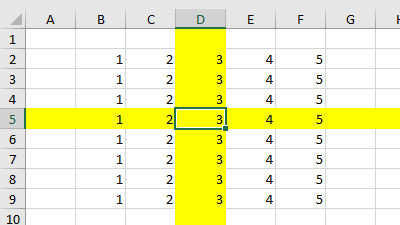
The following example clears the color in all the cells on the worksheet by setting the ColorIndex property equal to 0, and then highlights the entire row and column that contain the active cell by using the EntireRow and EntireColumn properties.
'------------------ Worksheet ------------------
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
On Error Resume Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
' Clear the color of all the cells
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
If Target.Cells.count > 1 Then Exit Sub
With Target
' Highlight the entire row and column that contain the active cell
.EntireRow.Interior.ColorIndex = 6
.EntireColumn.Interior.ColorIndex = 6
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubHighlight the Row and Column Within the Current Region
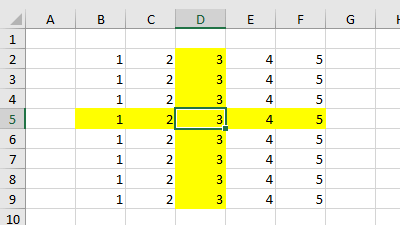
The following example clears the color in all the cells on the worksheet by setting the ColorIndex property equal to 0, and then highlights the row and column that contain the active cell, within the current region by using the CurrentRegion property of the Range object.
'------------------ Worksheet ------------------
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
On Error Resume Next
' Clear the color of all the cells
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
If IsEmpty(Target) Or Target.Cells.count > 1 Then Exit Sub
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
With ActiveCell
' Highlight the row and column within the current region
Range(Cells(.Row, .CurrentRegion.Column), Cells(.Row, .CurrentRegion.Columns.count + .CurrentRegion.Column - 1)).Interior.ColorIndex = 6
Range(Cells(.CurrentRegion.Row, .Column), Cells(.CurrentRegion.Rows.count + .CurrentRegion.Row - 1, .Column)).Interior.ColorIndex = 6
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubHighlight the Entire Row and Column with double-click
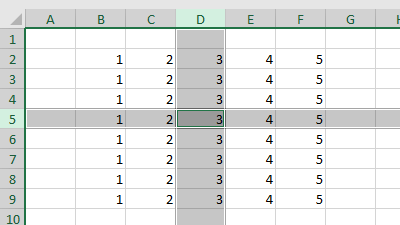
The following example highlights the entire row and column with a simple double-click.
'------------------ Worksheet ------------------
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
'Step 1: Declare Variables
Dim strRange As String
'Step2: Build the range string
strRange = Target.Cells.Address & "," & _
Target.Cells.EntireColumn.Address & "," & _
Target.Cells.EntireRow.Address
'Step 3: Pass the range string to a Range
Range(strRange).Select
End SubDownload
Download the Excel Macro: Highlight the Active Row and Column
How to Use This Macro
Most VBA code should be placed in Standard Modules unless specified.
If you see a comment '------------------ Modules------------------ in the code header that means put the code in a Standard Module. For more information, learn this course: Where should I put the Excel VBA code?
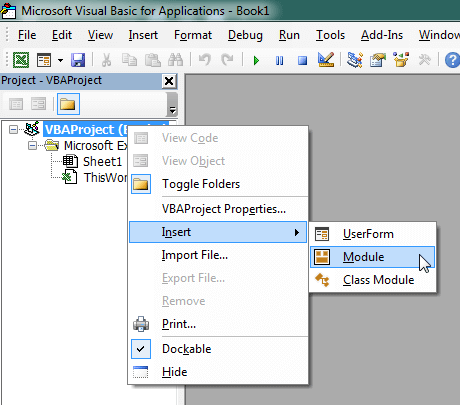
The following steps teach you how to put VBA code into a Standard Module:
- Activate the Visual Basic Editor by pressing ALT + F11.
- Right-click the project/workbook name in the Project Window.
- Choose Insert -> Module.
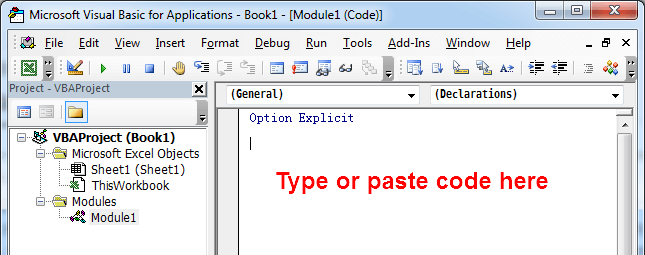
- Type or paste the code in the newly created module. You will probably need to change the sheet name, the range address, and the save location.
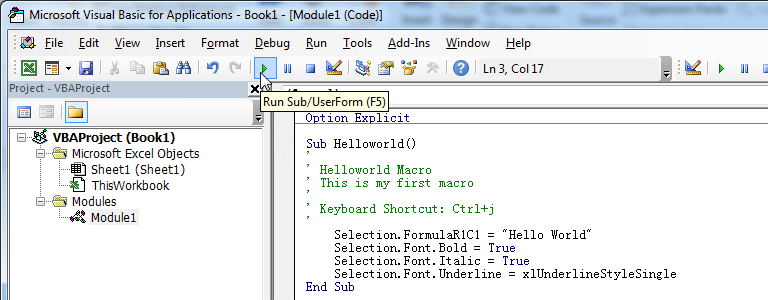
- Click Run button on the Visual Basic Editor toolbar.
- For more information, learn this course: Programming with Excel VBA